| boxglm |
Power transformations by Box-Cox method for GLMs |
boxglm |
SAS Macro Programs: boxglm
$Version: 1.1 (10 Dec 1991)
Michael Friendly
York University
Power transformations by Box-Cox method for GLMs
The boxglm macro finds power transformations of the response variable in a
general linear model by the Box-Cox method, with graphic display of the
maximum likelihood solution (RMSE plot), F-values for model effects (EFFECT
plot), and the
influence of observations on choice of power (INFL plot). The program produces
printer plots by default, and can optionally produce
high-resolution versions of any of these plots.
Method
The program uses transforms the response to all powers from
the LOPOWER= value to the HIPOWER= value, and fits a linear
model using PROC GLM for each, extracting values to an output dataset from
which the plots are drawn.
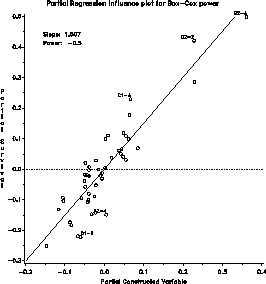
The influence plot also implements a score test for the power transformation
due to Atkinson, which provides an alternative estimate of the
power transformation. based on power = 1 - slope of the fitted line
in the partial regression plot for a constructed variable.
Usage
boxglm is a macro program. Values must be supplied for the
RESP= and MODEL= parameters.
The arguments may be listed within parentheses in any order, separated
by commas. For example:
%boxglm(resp=responsevariable, model=predictors, ..., )
Parameters
- RESP=
- The name of the response variable for
analysis.
- MODEL=
- The independent variables in the
model, i.e., the terms on the right side
of the = sign in the MODEL statement for PROC
GLM. The MODEL= argument should be spelled out
completely, rather than using abbreviated 'bar'
notation.
- CLASS=
- Specifies the MODEL= variables which are
classification factors rather than continuous variables.
- DATA=_LAST_
- The name of the data set holding the
response and predictor variables. (Default:
most recently created)
- ID=
- The name of an ID variable for observations
- OUT=_DATA_
- The name of an output dataset to contain
the transformed response. This dataset
contains all original variables, with the
transformed response replacing the original
variable.
- OUTPLOT=_PLOT_
- The name of the output data set containing
_RMSE_, and t-values for each effect in the
model, with one observation for each power
value tried.
PPLOT=RMSE EFFECT INFL
- Which printer plots should be produced?
One or more of RMSE, EFFECT, and INFL, or NONE.
- GPLOT=NONE
- Which high-resolution (PROC GPLOT) plots
should be produced? One or more of RMSE,
EFFECT, and INFL, or NONE.
- LOPOWER=-2
- low value for power
- HIPOWER=2
- high value for power
- NPOWER=21
- number of power values in the interval
LOPOWER to HIPOWER
- CONF=.95
- confidence coefficient for the confidence
interval for the power.
Example
The example finds power transformations for the SURVIVAL variable
in a dataset relating survival time to
type of poison and antidote used.
data poisons;
input antidote $ poison @;
label survival='Survival time';
length id $4;
do rep = 1 to 4;
id = trim(antidote)||trim(put(poison,1.))||'-'||put(rep,1.);
input survival @;
output;
end;
cards;
A 1 .31 .45 .46 .43
A 2 .36 .29 .40 .23
A 3 .22 .21 .18 .23
B 1 .82 1.10 .88 .72
B 2 .92 .61 .49 1.24
B 3 .30 .37 .38 .29
C 1 .43 .45 .63 .76
C 2 .44 .35 .31 .40
C 3 .23 .25 .24 .22
D 1 .45 .71 .66 .62
D 2 .56 1.02 .71 .38
D 3 .30 .36 .31 .33
;
*include macros(boxglm);
%boxglm(data=poisons,
resp=Survival,
model=antidote poison,
class=antidote poison,
id=id,
gplot=RMSE EFFECT INFL,
npower=17, conf=.99);
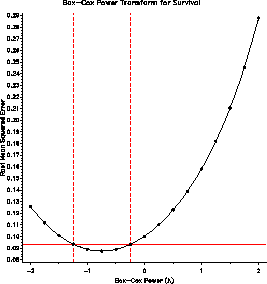
The plot of RMSE vs. lambda (power) indicates power = -1 / sqrt(SURVIVAL)
as the maximum likelihood estimate, but power = -1 / SURVIVAL == survival
rate is within the confidence interval.
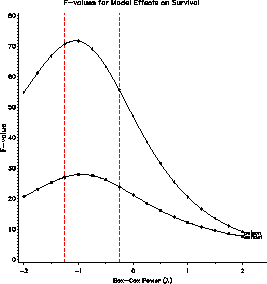
The EFFECT plot indicates that the significance of partial F-tests are unaffected by the choice of power.
The influence plot indicates that a few observations have a large leverage,
but none is influential in determining the choice of power.
See also
boxcox Power transformations by Box-Cox method
boxtid Power transformations by Box-Tidwell method
outlier Robust multivariate outlier detection
resline Resistant line for bivariate data
stars Diagnostic plots for transformations to symmetry


