SAS Macro Programs: inflplot
$Version: 1.2 (13 Feb 2006 15:38:11)
Michael Friendly
York University
Influence plots for regression models
The INFLPLOT macro produces a variety of influence plots for a regression
model -- plots of studentized residuals vs. leverage (hat-value),
using an influence measure (COOK's D, DFFITS, COVRATIO) as the size of
a bubble symbol. The plot show the components of influence (residual
and leverage) as well as their combined effect.
Plots can be produced either as bubble plots with PROC GPLOT or GCONTOUR
plots of any of the influence measures overlaid with bubble symbols.
The contour plots show how the influence measures vary with residual
and leverage. Horizontal reference lines in the plots delimit
observations whose studentized residuals are individually or jointly
(with a Bonferonni correction) significant Vertical reference lines in
the plot shows observations which are of ``high leverage''.
The INFLPLOT macro is defined with keyword parameters. The Y= and
X= parameters are required.
The arguments may be listed within parentheses in any order, separated
by commas. For example:
%inflplot(Y=response, X=X1 X2 X3 X4, ...);
- DATA=
-
The name of the input data set [Default:
DATA=_LAST_]
- Y=
-
Name of the criterion variable.
- X=
-
Names of the predictors in the model. Must be a blank-separated
list of variable names.
- ID=
-
The name of an observation ID variable. If not specified, observations
are labeled sequentially, 1, 2, ...
- BUBBLE=
-
Influence measure shown by the bubble size.
Specify one of COOKD, DFFITS, or COVRATIO [Default:
BUBBLE=COOKD]
- CONTOUR=
-
Specifies influence measures shown as contours in the plot(s).
One or more of COOKD, DFFITS, or COVRATIO.
- LABEL=
-
Points to label with the value of the ID variable in the plot:
One of ALL, NONE or INFL. The choice INFL causes only influential
points to be labelled. [Default:
LABEL=INFL]
- INFL=
-
Criterion for declaring an influential observation,
a logical expression using any of the variables in the
output
OUT= data set of regression diagnostics.
The default is
-
INFL=%STR(ABS(RSTUDENT) > TCRIT
OR HATVALUE > HCRIT
OR ABS(&BUBBLE) > BCRIT)
- LSIZE=
-
Observation label size. The height of other text is controlled by
the
HTEXT= goption. [Default: LSIZE=1.5]
- LCOLOR=
-
Observation label color [Default:
LCOLOR=BLACK]
- LPOS=
-
Observation label position, using a position value
understood by the Annotate facility. [Default:
LPOS=5]
- BSIZE=
-
Bubble size scale factor [Default:
BSIZE=10]
- BSCALE=
-
Scale for the bubble size.
BSCALE=AREA makes the bubble area
proportional to the influence measure; BSCALE=RADIUS makes the bubble
radius proportional to influence. [Default: BSCALE=AREA]
- BCOLOR=
-
Bubble color [Default:
BCOLOR=RED]
- HREF=
-
Locations of horizontal reference lines. The macro variables
HCRIT and HCRIT1 are internally calculated as 2 and 3 times the
average HAT value. [Default: HREF=&HCRIT &HCRIT1]
- VREF=
-
Locations of vertical reference lines. The program computes
critical values of the t-statistic for an individual residual
(TCRIT) or for all residuals using a Bonferroni correction
(TCRIT1) [Default: VREF=-&TCRIT1 -&TCRIT 0 &TCRIT &TCRIT1]
- REFCOL=
-
Color of reference lines [Default:
REFCOL=BLACK]
- REFLIN=
-
Line style for reference lines. Use 0 to suppress. [Default:
REFLIN=33]
- GPLOT=
-
Whether to draw the plot using PROC GPLOT, Y or N. This may be useful
if you use the
CONTOUR= option and want to suppress the GPLOT version.
- OUT=
-
The name of the output data set containing regression diagnostics
[Default:
OUT=_DIAG_]
- OUTANNO=
-
Output data set containing point labels [Default:
OUTANNO=_ANNO_]
- NAME=
-
The name of the graph in the graphic catalog [Default:
NAME=INFLPLOT]
- GOUT=
-
The name of the graphics catalog
%gskip Device-independent macro for multiple plots
This example produces an influence plot of a model
predicting FUEL consumption from the
predictor variables TAX, DRIVERS, ROAD, INCome, and POPulation.
%include macros(inflplot); *-- or include in an autocall library;
%include data(fuel) ;
title 'Fuel Consumption: Influence Plot';
%inflplot(data=fuel,
y=fuel,
x=tax drivers road inc pop,
id=state, bsize=14);
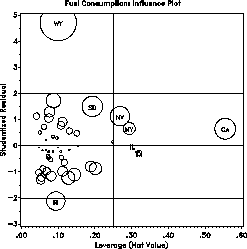 The plot indicates that WYoming and Rhode Island have large absolute residuals,
while CAlifornia is a high-leverage point.
The plot indicates that WYoming and Rhode Island have large absolute residuals,
while CAlifornia is a high-leverage point.
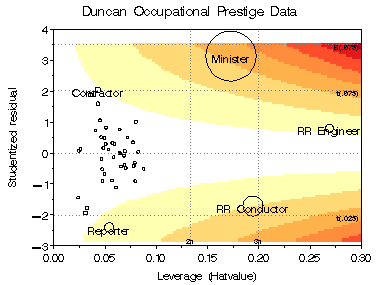
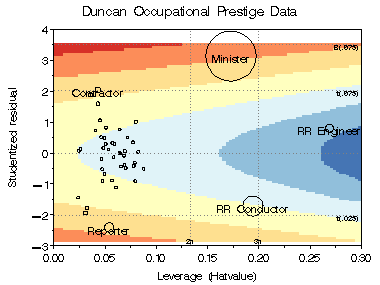
This example shows two contour plots of Cook's D and CovRatio for the Duncan data.
In both plots, bubbles are proportional to Cook's D.
%include macros(inflplot);
%include data(duncan) ;
%inflplot(data=duncan,
y=Prestige,
x=Income Educ,
id=job,
bubble=cookd,
bsize=14, lsize=2.5, bcolor=red,
out=infl, outanno=labels,
contour=cookd covratio, gplot=NO);
See also
gskipDevice-independent macro for multiple plots
cpplot Plots of Mallow's C(p) and related statistics for model selection
inflogis Influence plot for logistic regression models
outlier Robust multivariate outlier detection
partial Partial regression residual plots


