Visualizing Categorical Data: ordplot
$Version: 1.3 (9 Nov 2000)
Michael Friendly
York University
Diagnose form of discrete frequency distributions
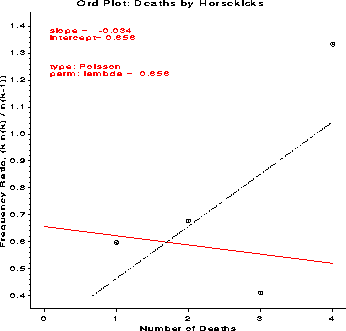
The ORDPLOT macro constructs a plot whose slope and intercept can diagnose
the form of a discrete frequency distribution. This is a plot of
k n(k) / n(k-1) against k, where k is the basic
count and n(k) is the frequency of occurrence of k. The macro
displays both a weighted and unweighted least squares line and uses the
slope and intercept of the weighted line to determine the form of the
distribution.
Method
The ORDPLOT macro is called with keyword parameters. The COUNT=
and FREQ= variables are required. The arguments may be listed within parentheses in
any order, separated by commas. For example:
%ordplot(data=horskick, count=Deaths, freq=corpsyrs);
Parameters
- DATA=
-
Name of the input data set [Default:
DATA=_LAST_]
- COUNT=
-
The name of the basic count variable
- FREQ=
-
The name of the variable giving the number of occurrences of COUNT
- LABEL=
-
Label for the horizontal (COUNT=) variable. If not specified the variable label for the COUNT= variable in the input data set is used.
- OUT=
-
The name of the output data set [Default:
OUT=ORDPLOT]
- NAME=
-
Name of the graphics catalog entry [Default:
NAME=ORDPLOT]
Example
%include vcd(ordplot); *-- or include in an autocall library;
data horskick;
input deaths corpsyrs;
label deaths='Number of Deaths'
corpsyrs='Number of Corps-Years';
cards;
0 109
1 65
2 22
3 3
4 1
;
%ordplot(data=horskick, count=Deaths, freq=corpsyrs);
This produces the plot below. The near-zero slope of the (red) weighted
least-squares line diagnoses this as a Poisson distribution.
See also
distplot Plots for discrete distributions
goodfit Goodness of fit tests for discrete distributions
poisplot Poissonness plot for discrete distributions
rootgram Hanging rootograms for discrete distributions
![[Previous]](../icons/previous.gif)
![[Next]](../icons/next.gif)
![[Up]](../icons/up.gif)
![[Contents]](../icons/contents.gif)
![[Search]](../icons/search.gif)
Previous: mosmat Next: panels Up: Appendix A Top: index.html
